1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| clc
clear
mu = 4*pi*1e-7;
T=logspace(-3,4,40);
rho=[10,200,10];
depth = [1,500,2000,100000];
h = diff(depth);
[apparentRho,Phase]=MT1DForward(rho,h,1./T);
Depth = sqrt((apparentRho.*T)./(2*pi*mu));
rho_H = apparentRho.*(180./(2*Phase)-1);
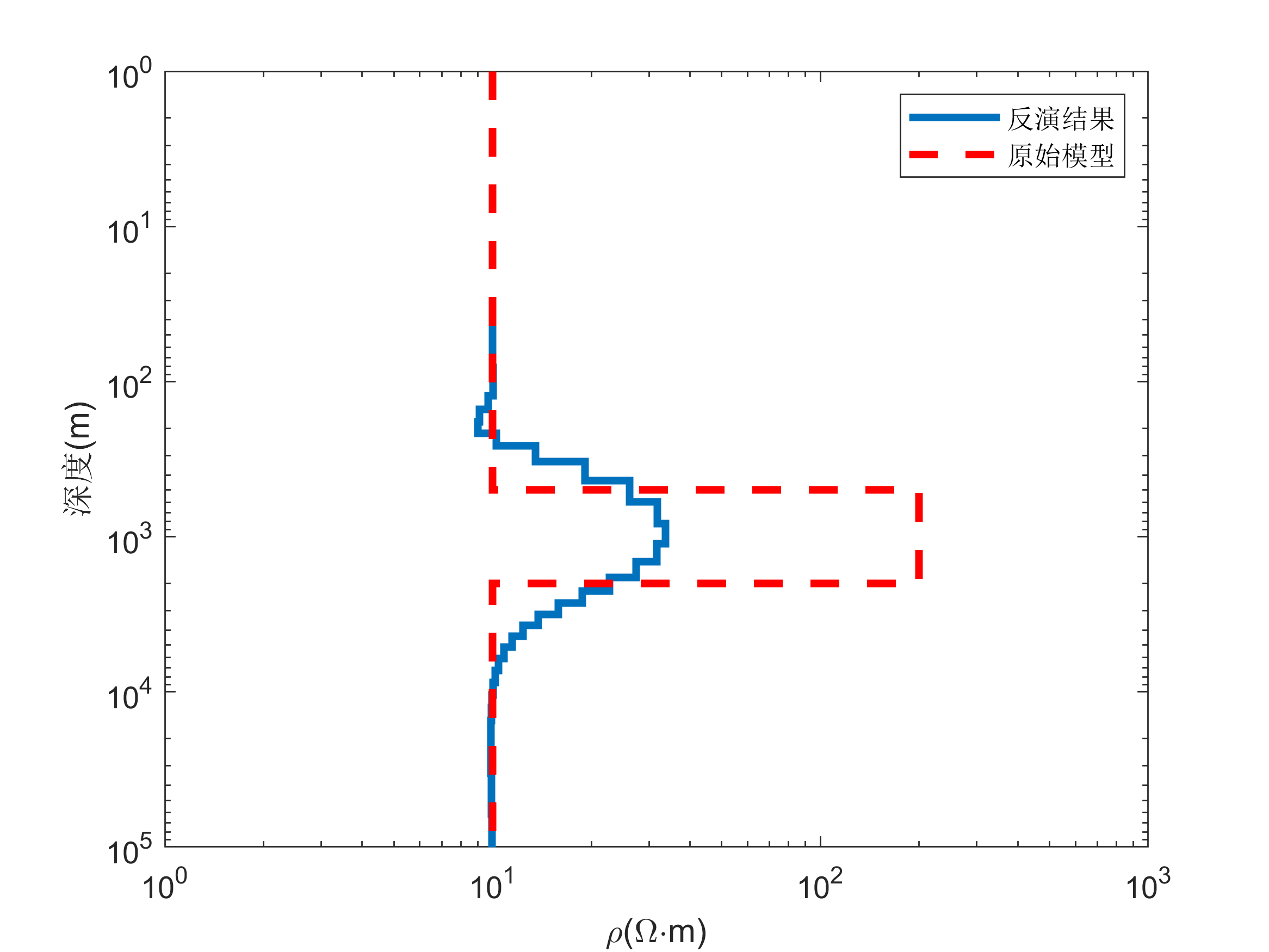
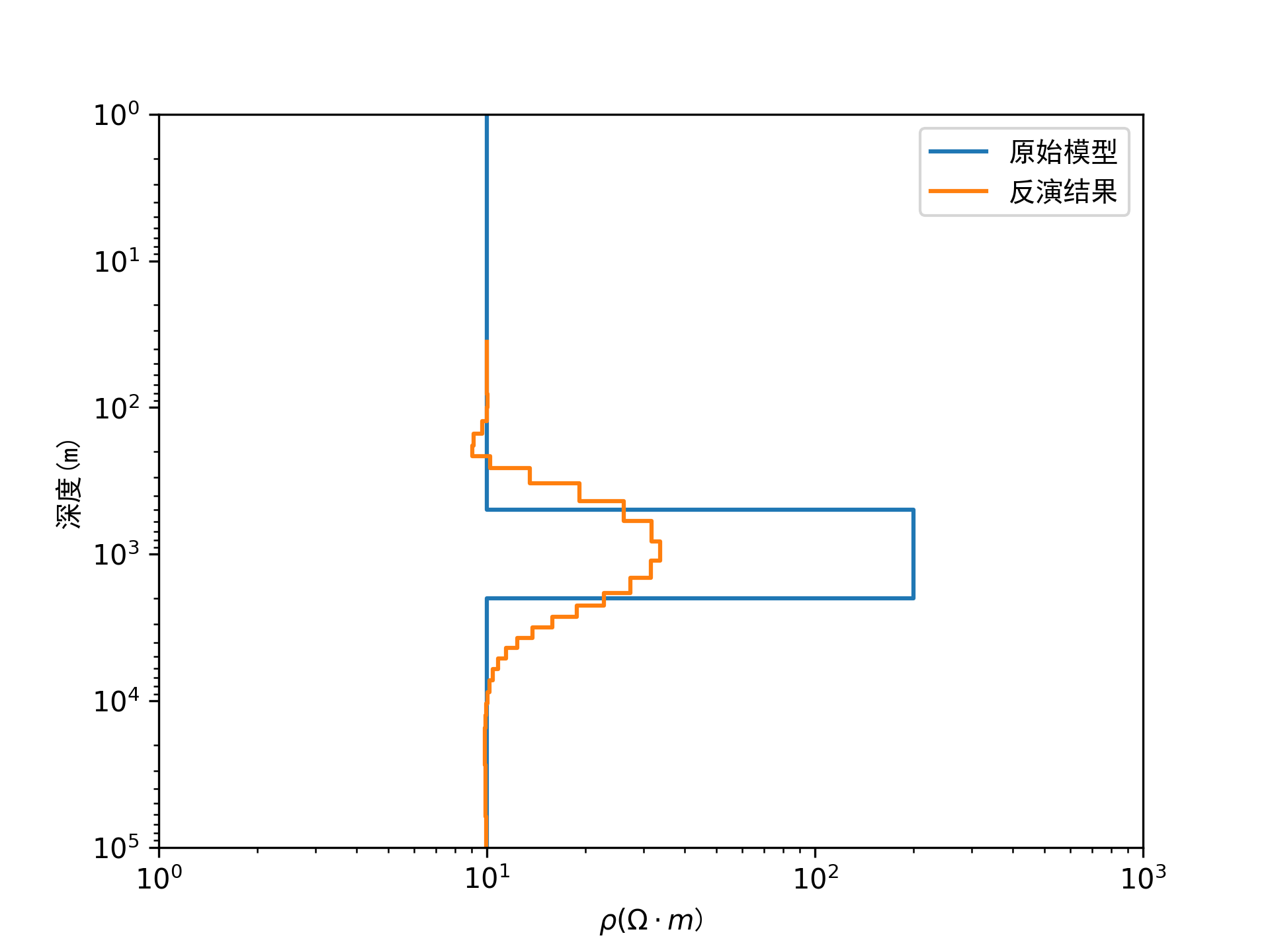
figure()
stairs(rho_H,Depth,'linewidth',2.5);
hold on
rho=[10,10,200,10];
stairs(rho,depth,'r--','linewidth',2.5);
set(gca,'xscale','log');
set(gca,'ydir','reverse','yscale','log');
xlim([1e0,1e3]);
ylim([1e0,1e5]);
xlabel('\rho(\Omega\cdotm)');
ylabel('深度(m)');
legend('反演结果','原始模型');
[apparentRho_inv,Phase_inv] = MT1DForward(rho_H,diff(Depth),1./T);
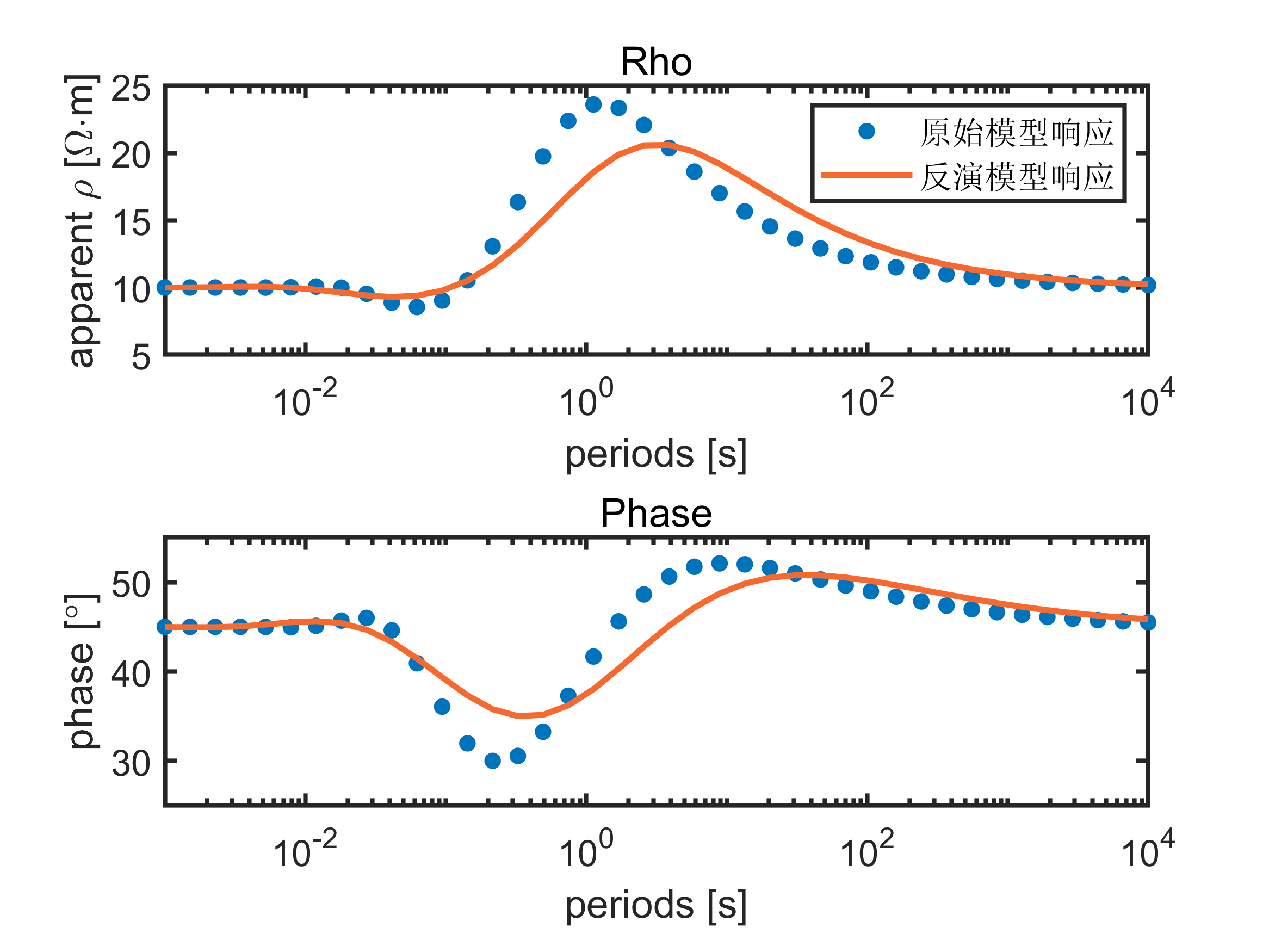
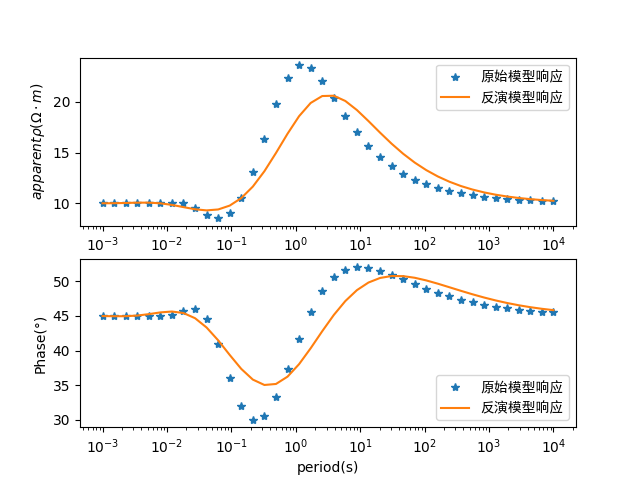
figure()
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(T,apparentRho,'o','MarkerSize',5,'MarkerFaceColor',[0,0.45,0.74])
hold on;
plot(T,apparentRho_inv,'-','MarkerSize',5,'color', [0.97 0.41 0.18],'LineWidth',2)
set(gca,'Xscale','log','LineWidth',1.5,'FontSize',12)
xlabel('periods [s]');
ylabel('apparent \rho [\Omega\cdotm]')
title('Rho');
axis([10^-3,10^4,5,25]);
legend('原始模型响应','反演模型响应');
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(T,Phase,'o','MarkerSize',5,'MarkerFaceColor',[0,0.45,0.74])
hold on;
plot(T,Phase_inv,'-','MarkerSize',5,'color', [0.97 0.41 0.18],'LineWidth',2)
set(gca,'Xscale','log','LineWidth',1.5,'FontSize',12)
xlabel('periods [s]');
ylabel('phase [\circ]');
title('Phase');
axis([10^-3,10^4,25,55]);
|